UMR Bandung 2025: Insights, Trends, and Economic Impact on Workers and Businesses
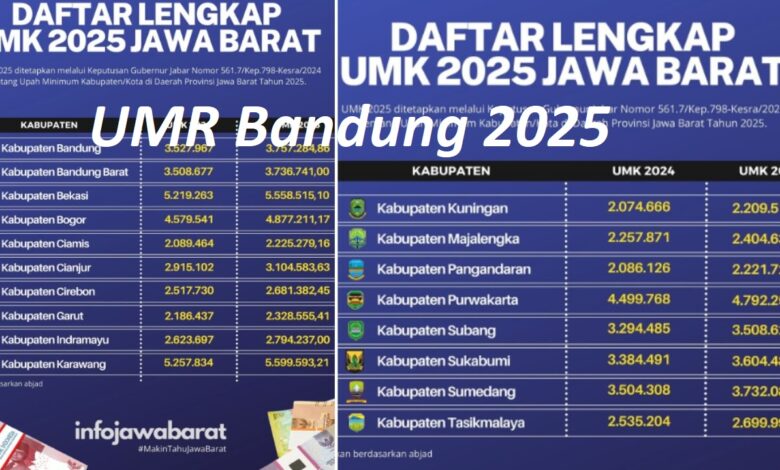
The topic of UMR Bandung 2025 has become a central point of discussion in West Java’s economic landscape. Every year, the determination of UMR—commonly understood as the minimum wage—affects millions of workers, thousands of businesses, and the broader economic ecosystem of the city. Bandung, known as the “Paris of Java,” is not only famous for its cultural vibrancy and innovation-driven youth but also for being one of the fastest-growing urban centers in Indonesia. As such, the conversation surrounding UMR Bandung 2025 extends far beyond numbers—it reflects the balance between fair living wages and sustainable business growth.
In this article, we will explore the meaning of UMR, its role in Bandung’s economy, the latest updates for 2025, the impact on industries and workers, as well as the broader implications for investment and development.
Understanding UMR in the Context of Bandung
UMR stands for “Upah Minimum Regional,” or the Regional Minimum Wage. In the Indonesian labor system, UMR is the benchmark wage level that employers must provide to employees, typically set annually by provincial or municipal governments. While today’s regulations often use terms like UMK (Upah Minimum Kota/Kabupaten) or UMP (Upah Minimum Provinsi), the term UMR is still widely used in daily conversation.
For Bandung, UMR represents more than just compliance with labor laws. It reflects the city’s socioeconomic dynamics, where cost of living, inflation, and productivity play major roles. Bandung, as the capital of West Java, has unique challenges compared to smaller towns or rural districts. It is a hub of education, creative industries, tourism, and manufacturing, all of which contribute to different wage demands.
The Economic Landscape of Bandung in 2025
UMR Bandung 2025 stands as a city shaped by rapid urbanization, digital transformation, and a vibrant creative economy. The city is a magnet for students, entrepreneurs, and investors, creating a complex mix of opportunities and challenges.
Key aspects shaping Bandung’s economy include:
- Creative and digital industries: Startups, software developers, and fashion designers thrive in Bandung’s innovation-friendly culture.
- Tourism and hospitality: Hotels, cafes, and cultural attractions continue to fuel demand for service workers.
- Manufacturing and industry: Factories in and around Bandung still employ large numbers of workers, particularly in textiles and garments.
- Education sector: With dozens of universities, Bandung attracts a young, educated workforce eager to contribute to the economy.
These sectors directly interact with the UMR, as they must balance the need to attract talent with the realities of operating costs.
UMR Bandung 2025: The Official Adjustment
Each year, government authorities consider multiple factors before setting the new UMR. These include inflation rates, economic growth, productivity levels, and the capacity of businesses to sustain wage increases.
For 2025, UMR Bandung reflects an effort to maintain fairness for workers while ensuring businesses remain competitive. The increase acknowledges the rising cost of living in Bandung, where housing, transportation, and daily necessities have become more expensive in recent years.
The adjustment also demonstrates the government’s attempt to balance national policies with local realities. Bandung’s UMR is often higher than that of surrounding districts, reflecting its urban cost structure and its role as a major metropolitan center.
Factors Influencing UMR Bandung 2025
Several key elements drive the determination of UMR Bandung 2025:
Cost of Living
Bandung has experienced steady increases in living expenses, particularly in housing, food, and transportation. Urban lifestyles demand higher wages to ensure workers can meet their basic needs.
Inflation
Inflationary pressures, whether from global markets or local supply chains, directly affect wage calculations. The 2025 adjustment accounts for projected inflation to prevent workers’ purchasing power from declining.
Economic Growth
Bandung’s economy shows resilience, supported by its diversified sectors. A healthy growth rate provides room for wage increases without destabilizing businesses.
Productivity and Skills
The city’s workforce is increasingly skilled, particularly in technology and design. Employers recognize the value of paying competitive wages to attract and retain talent.
Business Sustainability
While higher wages benefit workers, authorities must ensure businesses—especially small and medium enterprises—can afford the increase without reducing staff or relocating.
The Impact of UMR Bandung 2025 on Workers

For workers, the UMR adjustment is more than just a figure; it is the foundation of livelihood. The increase in 2025 offers several benefits:
- Improved living standards: Higher wages allow workers to cover essentials, from rent to food, while also saving or spending on leisure.
- Increased motivation and productivity: Fair compensation often leads to better performance, loyalty, and workplace satisfaction.
- Access to opportunities: Competitive wages in Bandung attract skilled workers from surrounding areas, raising the overall talent pool.
However, challenges remain. Not all workers will benefit equally, as wage adjustments often apply primarily to entry-level or less-experienced employees. Skilled workers may demand higher salaries beyond the UMR benchmark.
The Impact on Businesses in Bandung
Businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises, face both opportunities and challenges with the new UMR Bandung 2025.
- Operational costs rise: Employers must allocate larger budgets to cover wages, impacting pricing strategies and profit margins.
- Employee retention improves: Competitive pay helps businesses keep skilled staff, reducing turnover and training costs.
- Innovation is encouraged: To absorb higher labor costs, many businesses explore efficiency, automation, and digital solutions.
- Uneven impact by sector: Labor-intensive industries such as manufacturing and hospitality face heavier burdens compared to technology-driven businesses.
Bandung’s Position Compared to Other Regions
When examining UMR Bandung 2025, it is useful to compare with other regions in West Java and beyond. Bandung often has one of the higher minimum wages in the province, reflecting its urban dynamics. Neighboring districts may have lower UMRs, which sometimes creates challenges as businesses consider relocating to reduce costs.
Yet Bandung’s higher UMR also signals its strength as a premium labor market, attracting talent and fostering innovation. For many companies, the advantages of being based in Bandung outweigh the wage differences.
Broader Implications for Bandung’s Development
The UMR Bandung 2025 is not just about wages; it reflects the city’s trajectory of development. A fair minimum wage supports social stability, reduces inequality, and stimulates local consumption. Workers with more disposable income contribute to local businesses, fueling economic cycles.
At the same time, authorities must remain vigilant about potential downsides, such as rising operational costs or business relocations. The success of UMR Bandung 2025 depends on policies that support small businesses, promote skill development, and encourage innovation.
Worker Perspectives on UMR Bandung 2025
Workers often view UMR not only as a legal standard but also as a symbol of recognition for their efforts. In Bandung, many employees express cautious optimism. While the increase is welcome, they also highlight the rising costs of housing and urban necessities. Some workers feel that while UMR Bandung 2025 improves their financial security, it is still a baseline rather than a guarantee of comfort.
For fresh graduates and new workers, the UMR provides a starting point in their careers. For more experienced employees, the focus shifts to opportunities for growth beyond the minimum wage.
Business Perspectives on UMR Bandung 2025
Employers in Bandung show mixed responses. Larger corporations with established revenue streams can absorb the wage increase more smoothly. However, small businesses in retail, hospitality, and manufacturing express concerns about tight margins.
Some business owners view the new UMR as a chance to re-evaluate their operations, exploring digital transformation and new revenue models. Others worry about potential downsizing or relocating to areas with lower wage requirements.
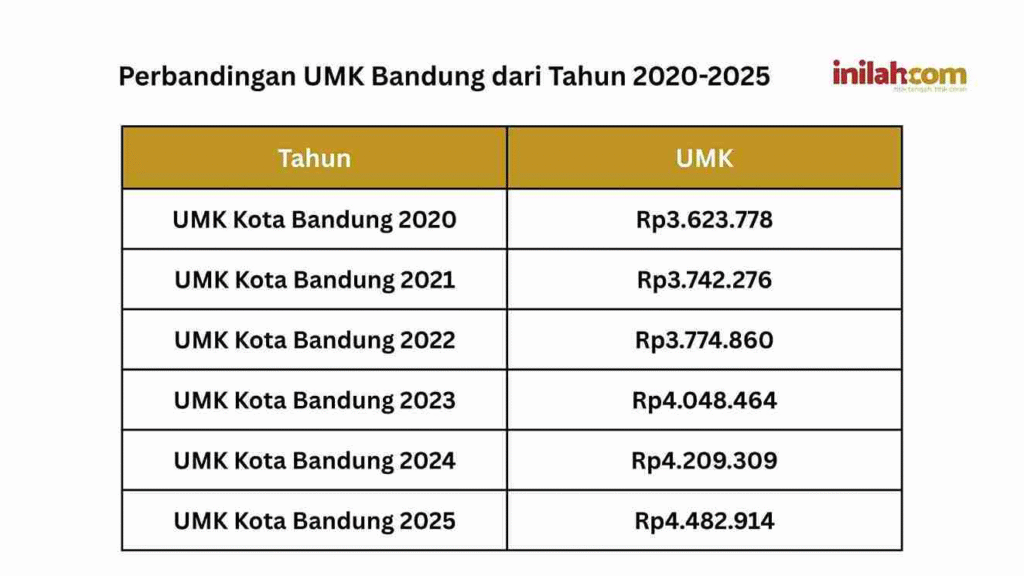
Long-Term Outlook of UMR Bandung
The trajectory of UMR Bandung reflects larger economic shifts in Indonesia. With Bandung’s growing reputation as a creative and technological hub, wages are expected to continue rising over the long term. This positions the city as a place where innovation meets fair labor practices.
However, the long-term success depends on three pillars:
- Balanced wage policies that consider both workers’ welfare and business sustainability.
- Investment in skills and education, ensuring the workforce remains competitive in a digital economy.
- Support for small businesses, which form the backbone of Bandung’s economy.
Preparing for the Future: Workers and Employers
To navigate UMR Bandung 2025 effectively, both workers and employers must adopt forward-looking strategies.
For workers:
- Invest in skills development to move beyond the minimum wage bracket.
- Manage personal finances wisely to maximize the benefits of wage increases.
- Stay informed about labor rights and opportunities.
For employers:
- Embrace efficiency and innovation to absorb higher labor costs.
- Build strong relationships with employees through fair pay and growth opportunities.
- Collaborate with government and industry associations to find sustainable solutions.
Conclusion
The determination of UMR Bandung 2025 represents more than an annual adjustment; it is a reflection of Bandung’s dynamic economy, social priorities, and vision for the future. For workers, it is a symbol of fair compensation and a step toward better living standards. For businesses, it is a challenge and an opportunity to innovate and adapt.
Bandung continues to stand as a city of ideas, creativity, and resilience. As UMR Bandung 2025 takes effect, the city’s ability to balance economic growth with social equity will shape its role as a leader in West Java and beyond.
The conversation around UMR will never be limited to numbers; it will always be about people, progress, and the pursuit of prosperity.



